It depends on the system design. Sometimes one has to (still) use a dedicated net just for servos but that is old. Different fieldbuses and/or servo drive interfaces may support a partial frame; for example, one may only be able to set a control word which might be position or torque command while some may support a full parameter frame or command set which exposes a plethora of servo parameters and variations between the two extremes. Speed is also a consideration i.e. may only be fast enough to do motion control or fast enough to close a servo torque loops and/or fast enough to incorporate feedback devices e.g. force or range sensors (without wiring directly to the servo drive) - again, how fast? There's obviously a difference between a lumbering 100 horse motor and a low inertia voice coil motor. There's also the issue of how many servos (along with other I/O) can be handled at one time and whether or not safety I/O is (ideally) incorporated into the servo net.
There's also a dichotomy in basic control ideas i.e. embed servo loops entirely within the drive, within a motion controller or within the PLC or PC and, of course, somewhere in-between. Obviously, closing the loop at higher levels demands faster, more robust and more deterministic communication performance; it also demands faster and deterministic scan times in the controller: e.g., for precision work, closing torque loops at 30-40 kHz. Control networks that provide real time clock distribution and time-stamped I/O are helpful (in maximizing determinism) as well as control schemes that support interpolation. An interesting variation is distributed I/O slices that perform motion control and may even support smaller motors without a drive or with only an external power driver module.
The etherCAT which is a general purpose field bus which has been demonstrated to close the loop on a large number of servos concurrently which would seem to be going in right direction.
Products and reference designs of Servo drive communication module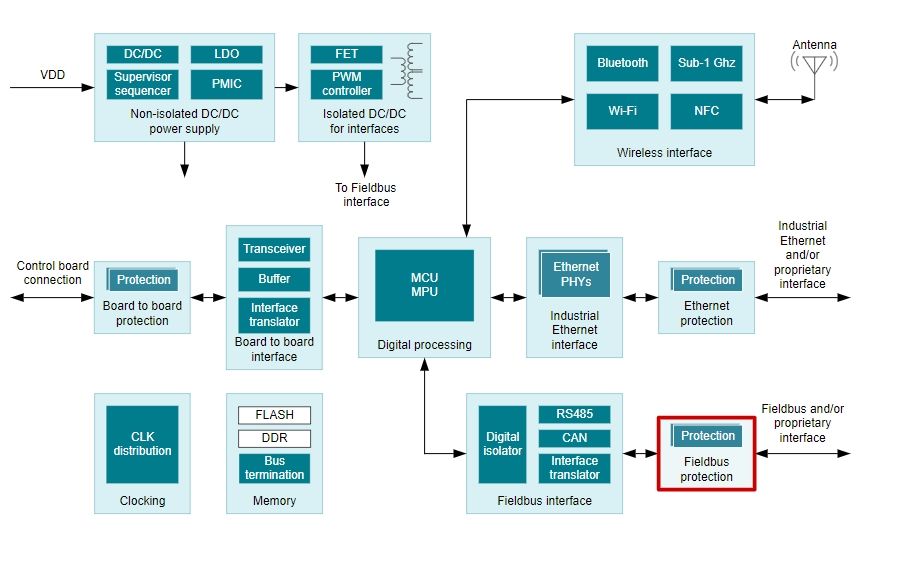
Non-isolated DC/DC power supply
Non-isolated DC/DC power supply is used to generate the various supply rails needed by the system to function. In general it comprises of DC/DC converters and linear regulators. Power supply supervisors are used to monitor the supply health. Complex systems require very specific power-up and power-down sequencing in order to guarantee reliable operation, better efficiency and overall system health. Power supply sequencers are required for this function. Non-isolated DC/DC power supply includes Buck converters (integrated switch)、Supervisor & reset ICs、Multi-channel ICs (PMICs)、eFuses & hot swap controllers、High-side switches、Linear & low-dropout (LDO) regulators、Boost converters (integrated switch)、Sequencers、Buck modules (integrated inductor), the Corresponding products are TPS62A01A、TPS3840、TPS51206、TPS2663、TPS27S100、TPS709、TPS61376、LM3881、TPSM828511
Isolated DC/DC interface
Input and output interfaces are often isolated to avoid ground loops. The local power supply requires an isolated DC/DC converter to generate isolated rails for these isolated interfaces. Isolated DC/DC interface includes Isolated DC/DC converters & modules、PWM controllers、Shunt voltage references、Transformer drivers, the Corresponding products are LM25018、UCC2809-1、ATL431LI、SN6501
Wireless interface
In motor drives typical wireless communication protocols are NFC and BLE (for service or maintenance interfaces). Sub-1 GHz is used for long distance communication. Wireless interface includes Low-power 2.4-GHz products、Wi-Fi products、Other wireless products, the Corresponding products are CC2651R3、WL1837MOD、CC2620
Board-to-board protection
Either protection steering diodes or TVS is needed to clamp the voltage during an ESD or surge event to avoid damage to electrical circuits behind the protection. Board-to-board protection includes ESD protection diodes, the Corresponding products are TPD2E007、TPD6E001、TPD4S012
Board-to-board interface
Wired signal interfaces like LVDS, RS485, CAN, interface translators or buffer transceivers are important for robust communication between the communication module and the control module. Board-to-board interface includes RS-485 & RS-422 transceivers、LVDS, M-LVDS & PECL ICs、RS-232 transceivers、Noninverting buffers & drivers、Direction-controlled voltage translators、Inverting buffers & drivers, the Corresponding products are THVD1520、SN65MLVD203、MAX3232E、SN74LVC1G17、SN74AXC4T774、SN74AHC1G04
Digital processing
Host processor should support multiple Ethernet and Fieldbus communication protocols. Ethernet/IP, EtherCAT, Profinet, Profibus, PowerLink, Sercos 3 and more are both in master and slave configurations. Digital processing includes Arm-based processors, the Corresponding products are AM6526、AM3358、AM3359
Industrial Ethernet interface
Wired signal interfaces like 10/100 Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet are important for deterministic, secure and reliable communication between the drive and external systems like PLC, motion controllers or other drives on the factory floor. Many industrial drives need to support multi-protocol Ethernet and meet the IEC61800-3 EMC immunity requirements for robust communication in harsh industrial environments. Industrial Ethernet interface includes Ethernet PHYs, the Corresponding products are DP83822H、DP83822I、DP83869HM
Ethernet protection
Either protection steering diodes or TVS is needed to clamp the voltage during an ESD or surge event to avoid damage to electrical circuits behind the protection. Ethernet protection includes ESD protection diodes, the Corresponding products are TPD2E007、TPD6E001、TPD4S012
Clocking
High timing accuracy is required for real time communication protocols. Running several clock sources for different devices results in phase shift between the clocks, which accumulates over time. This can be avoided by adding a clock distribution network. Clocking includes Clock generators、Clock buffers, the Corresponding products are CDCE913、CDCLVC1102
Memory
Double Data Rate (DDR) memory has become more common in electronic systems as they provide faster data transfer and overall higher system performance. Conventional passive bus termination resistance is used for matching DDR termination line impedance to source impedance and thus reduces the amplitude of reflection to 0. ; ;Active DDR termination is used not only to reduce power dissipation (50% at 50% duty cycling,) but also improves data read/write accuracy & integrity. Memory includes DDR memory power ICs, the Corresponding products are TPS7H3302-SP、TPS7H3302-SEP
Fieldbus interface
Wired signal interfaces like RS485, CAN or interface translators are important for deterministic, secure and reliable communication between drive and external systems like PLC, motion controllers or other drives on the factory floor. Many industrial drives need to support Fieldbus solutions like Profibus, Modbus, Sercos or vendor specific protocols and need to meet the IEC61800-3 EMC immunity requirements for robust communication in harsh industrial environment. Isolated communication link is sometimes required to prevent ground loops. Fieldbus interface includes RS-485 & RS-422 transceivers、LVDS, M-LVDS & PECL ICs、RS-232 transceivers、Isolated RS-485 transceivers、Isolated CAN transceivers、Digital isolators, the Corresponding products are THVD1550、DS90LV001、MAX3232E、ISO1176、ISO1050、ISO7842
Fieldbus protection
Either protection steering diodes or TVS is needed to clamp the voltage during an ESD or surge event to avoid damage to electrical circuits behind the protection. Fieldbus protection includes ESD protection diodes, the Corresponding products are TPD2E007、TPD4S012
Previous: Electric power steering (EPS)